Headings
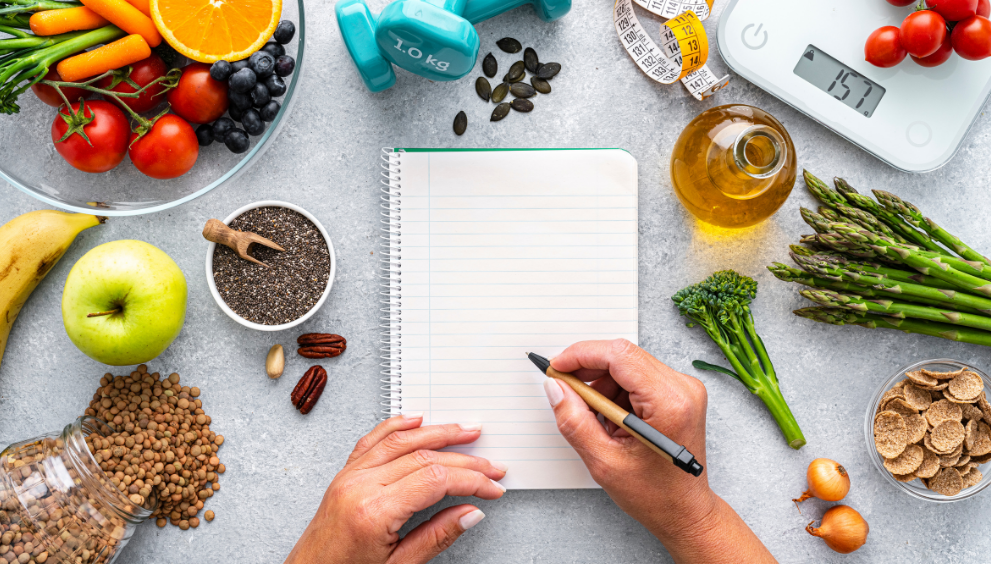
Diet is an essential part of healthy living. Choosing the right nutrition and appropriate diet types is critical for meeting the body’s needs, managing weight, and improving overall health. In this article, we will discuss four popular and effective diet types. We will detail the features of each diet type, their health benefits, and their applicability to help you determine which diet type is best for you.
1. Mediterranean Diet
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating habits of countries in the Mediterranean region. This diet type emphasizes healthy foods such as olive oil, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and nuts.
Key Components
- Olive Oil: Rich in healthy fatty acids, olive oil is a staple of the Mediterranean diet.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Colorful and diverse fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Whole Grains: Whole grain bread, rice, and pasta are preferred over white bread.
- Fish and Seafood: It is recommended to consume fish at least twice a week.
- Nuts and Seeds: Healthy snacks like walnuts, almonds, and chia seeds are included in this diet type.
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: The Mediterranean diet includes healthy fats and fiber-rich foods, which reduce the risk of heart diseases.
- Weight Control: Low processed food consumption and high fiber intake help in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Brain Health: Research suggests that this diet type may have protective effects against Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
Applicability
The Mediterranean diet is suitable for those who want to adopt a healthy and balanced lifestyle. It can also be enriched with various recipes, making it enjoyable and easy to follow.
2. Ketogenic Diet
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a diet type that emphasizes low carbohydrates, high fats, and adequate protein intake. The primary aim of this diet type is to induce ketosis in the body, allowing it to use fats as an energy source.
Key Components
- Low Carbohydrates: A daily intake of only 20-50 grams of carbohydrates is targeted.
- High Fats: The fat intake is increased to meet energy needs. Healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado oil, and butter are favored.
- Adequate Protein: Sufficient protein is consumed from sources like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
Health Benefits
- Weight Loss: The ketogenic diet promotes rapid weight loss by enhancing fat burning.
- Low Blood Sugar: Reduced carbohydrate intake helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for diabetics.
- Increased Energy: Once the body begins to use fats as an energy source, energy levels tend to rise.
Applicability
The ketogenic diet relies on carbohydrate restriction and can be challenging initially. However, those interested in this diet type need to prepare and plan accordingly.
3. Vegan Diet
What is the Vegan Diet?
The vegan diet is a diet type that completely excludes animal products. This diet type focuses on the consumption of plant-based foods.
Key Components
- Vegetables and Fruits: The vegan diet includes a variety of vegetables and fruits.
- Grains and Legumes: Healthy carbohydrate sources like rice, quinoa, lentils, and beans are preferred.
- Nuts and Seeds: Foods like walnuts, almonds, chia, and flax seeds provide healthy fats and protein.
- Plant-Based Milk and Meat Alternatives: Instead of dairy, plant-based milks (soy milk, almond milk) and alternatives like tofu and tempeh are used.
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: The vegan diet supports heart health due to its low saturated fat content.
- Weight Control: Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories, which can help with weight management.
- Cell Health: Fruits and vegetables are high in antioxidants and fiber, supporting cellular health.
Applicability
The vegan diet is suitable for individuals who do not consume meat and dairy products. However, careful planning is necessary to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
4. Intermittent Fasting
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is a diet type based on alternating periods of eating and fasting. This diet type aims to improve metabolism and assist with weight management.
Key Methods
- 16/8 Method: This involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window. For example, you can eat from 10 AM to 6 PM.
- 5:2 Method: Eat normally for five days a week, and restrict calorie intake to 500-600 calories on two days.
- Alternate Day Fasting: One day of normal eating followed by a day of fasting.
Health Benefits
- Metabolism Boost: Intermittent fasting may accelerate metabolism and enhance fat burning.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Lower insulin levels can reduce fat storage.
- Mental and Cognitive Health: Fasting may promote mental clarity and focus.
Applicability
Intermittent fasting requires establishing a habit of eating within specific time frames. However, while implementing this diet type, it is essential to focus on balanced and healthy eating.
Conclusion
Choosing the right diet types is important for leading a healthy life. The four diet types mentioned above — Mediterranean diet, ketogenic diet, vegan diet, and intermittent fasting — each offer different eating habits and health benefits. Determining which diet type is best for you depends on your personal goals, lifestyle, and health status.
When applying these diet types, it is essential not to forget to maintain balanced nutrition and to consume the necessary nutrients. By listening to your body and making appropriate plans, you can achieve your health goals. Remember that each individual’s nutritional needs are different; therefore, it is important to seek expert advice before trying a new diet type. By having the necessary information and resources for a healthy life, you can make a fresh start in your life.